Fighting in the city of Kunduz in north-eastern Afghanistan ended on 8 August. During the clashes, we transformed our office space into a temporary trauma unit to treat the people wounded. That unit is now closed and on 16 August all patients were transferred to the nearly-finished Kunduz Trauma Centre that our teams have been building since 2018. The local community still requires trauma care. A medic from our Kunduz team describes their experience during the fighting and the work that is going on today.
It is busy but calm, we’re recruiting new staff, and the final parts of finishing the hospital construction are happening all around us. But first things first – starting with the evening when the fighting erupted in Kunduz city…
That first evening there was continuous bombardment and shooting so we had to rush to the bunker and we stayed there all night, without any sleep. Patients were not able to reach the trauma unit at that stage, on account of the non-stop fighting in the streets.
The following morning, we got news of multiple victims arriving to the unit, but we could not get there because there was fighting in the street between where we were staying and the unit. Our colleagues were asking for our help urgently because they had a patient who had a gunshot wound in his chest and stomach who needed to go to surgery immediately and they needed assistance for that.
A moment came when the guns were quieter and it was possible to move – three of us ran to the other side of the road to the operating theatre.MSF medic in Kunduz
A moment came when the guns were quieter and it was possible to move – three of us ran to the other side of the road to the operating theatre. The patient had just lost their pulse, so we started chest compression while the anaesthetist was looking for an airway. I cut two holes in the chest – to make sure blood could drain out and to allow the lungs to expand; meanwhile another colleague was trying to stop the bleeding below the sternum. We could tell pretty quickly that the bullet had probably hit part of the heart, and it soon became clear that there was no way that we could save him.
Hard days
That was the start of our day of hell. And the first moment of our team being completely overwhelmed. There were a lot of other victims who came in and had to go to surgery: a lot of gunshot-wounded coming in; a lot of people injured by bomb blasts; and a lot of people caught in the crossfire.
It was a very long day. Many of our staff could not reach the trauma unit. The night-shift staff worked through the day. Some would take naps and sleep while others worked so we could keep staff going from morning and into the night.
At about 6:30am the next morning an ER doctor called me on the radio, saying “I need your help now”. As the fighting had receded a bit at that moment, I ran with the surgeon across the road. When we got into the unit it was crammed.

Four patients urgently needed emergency surgery – at the same time. We started doing lifesaving surgery on two patients, meanwhile we were doing everything possible to keep the other two alive. The two who were waiting survived and we could proceed to operate on them.
In the end one patient died, but three survived, which is still quite impressive – they all had very severe gunshot wounds and bomb blast injuries. While waiting for space to open up in the operating theatre, all the while trying to keep the other two alive in the emergency room, we still needed to assist other patients who had come in and needed care. We tried to assist them in between working on the emergency cases. So, this was a heavy day to get through.
An unexpected case
One of our patients was a young boy. He was brought by his father to the ER with a bandage already on his arm. He wasn’t crying and was just very silently looking ahead. I was supervising the ER along with the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) nurse. The boy looked comfortable and very much OK. There was no immediate urgency.
Because the fingers sticking out of the bandage looked well circulated and warm, I took my time in demonstrating to the staff how to do a proper investigation of the hand for nerve damage. Strangely enough the boy didn’t seem to feel anything on his whole hand, which suggested all three different nerves were cut.
I remember the moment the bandage opened and I just saw a gaping hole in the forearm of this child. There was more of the hole than tissue remaining.MSF medic in Kunduz
I continued and was gently unwrapping the bandage from his arm. I remember the moment the bandage opened and I just saw a gaping hole in the forearm of this child. There was more of the hole than tissue remaining. The father told me that a stray bullet had hit him while the kid was playing.
I remember the faces of the staff. Their expressions just said: well I didn’t expect that! And nor had I. So we packed up the wound again and tried to stabilise the hand, as it was as unstable as a hand can be. For some reason the only thing remaining was the artery going all the way to the fingers, but the nerves were all broken.
Medically, we all agreed that amputation was probably the best option. The father didn’t agree with this. He wanted to give it a chance. We did our best to debride [clean] the wound and keep the tissue alive, and attached an external fixator (a metal bracket to hold the bones in place while mending) to try to let it heal for as long as possible.
Up until today the boy’s hand is still there. He will never have a good hand again, that’s for sure. But the hand’s still there and that’s already something that we didn’t expect. The father has been very friendly but the little boy knows that if a doctor comes close, it means there is going to be pain. He hasn’t smiled at any of us, but we can see him smiling at his father.
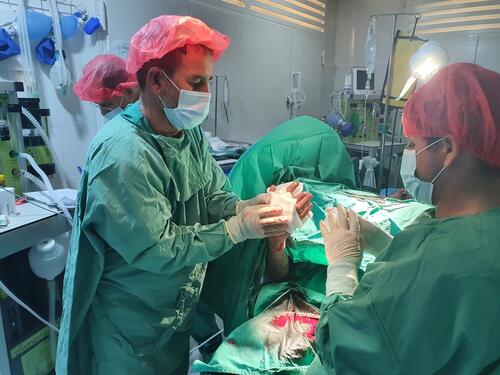
Calm – but still busy
As the fighting lessened, we began to see more patients coming in. Many of them had already received some sort of emergency treatment. When they had sustained an injury, they had gone to the nearest hospital where they could be taken care of and the medics there did what they could.
We are seeing an increase of people being referred to us from provincial hospitals, where patients had multiple surgeries. And they end up in our ER. Quite often we go into surgery and realise that there are not many options for us – there is not much more we can do to try to save the person. Still trying though; trying to stabilise; trying to get things in order with some surgery.
Moving to the new hospital
Here in Kunduz the rebuilding of our hospital has been going on for quite a while. The community has been waiting for the hospital to open up. Two weeks ago we transferred the patients from our temporary clinic to the hospital for the first time. This is new. It is a huge step to open the hospital, although it is not completely finished yet.

What we see in terms of patients coming is shifting from the very active gunshot and bomb blast injuries. Now mostly we see complications with the war wounded who need follow-up from previous treatment and also road traffic accidents, which are increasing sharply as things opens up again. Everyone here drives on their motorcycles without a helmet; when they fall, they suffer head traumas, which is not the best thing for us to treat as we don’t have neurosurgeons, so sometimes there is little we can do.
Making it work
In the Kunduz Trauma Centre, we’re doing our medical work while the construction is still going on. But the speed at which all the construction team and others are fixing things is quite amazing. They have a real approach of solving problems. We saw a stretcher bearer going to get a patient and having problems passing the stretcher over the uneven ground because there’s too much rubble. In no time, there were people putting concrete over the rubble. It’s quite incredible how the construction team are helping to fix all the problems our medical staff encounter.
We saw a stretcher bearer going to get a patient and having problems passing the stretcher over the uneven ground because there’s too much rubble.MSF medic in Kunduz
We have the same support from the team who are responsible for the hospital compound. One of them is always on a bicycle, cycling from one department to the other, fixing things incredibly rapidly. Same for supply, you just see medical items and supplies suddenly appearing at the front step of the departments, and a bit later there’s another doorstep bearing gifts of other packages for us to treat patients.
There is also the recruitment element – we’re increasing again. We have exams for staff going on; and we’re hoping to start recruiting mental health officers, which is something that we badly need.
And that’s how it feels for the moment – all the team really helping each other, together, trying to just make it work.